- Core Functions
- Application of product for heating
- Comparison for heating methods
Core Functions
- High efficiency heating
- Health function : Cell activation, metabolic activation, disease prevention, body heavy metal release, sleeping effect.
- Cosmetic effect : strengthening skin elasticity, lipolysis, and blood circulation improvement effect.
- Bactericidal effect : eradication of bacteria (ticks, fungi)
- Air purifying and dehumidifying function

Product Specification
| Item | Model name | Size(mm) | Thickness(mm) | Packing unit(M) | Power consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating use | T-1500-TL | 1500×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 300W |
| T-1000-TL | 1000×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 200W | |
| T-750-TL | 750×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 150W | |
| High-temperature use | T-750-TH | 750×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 500W |
| T-380-TH | 380×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 300W | |
| Mat use | T-750-TM | 750×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 120W |
| T-1500-TM | 1500×1000 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 250W |
Application Examples
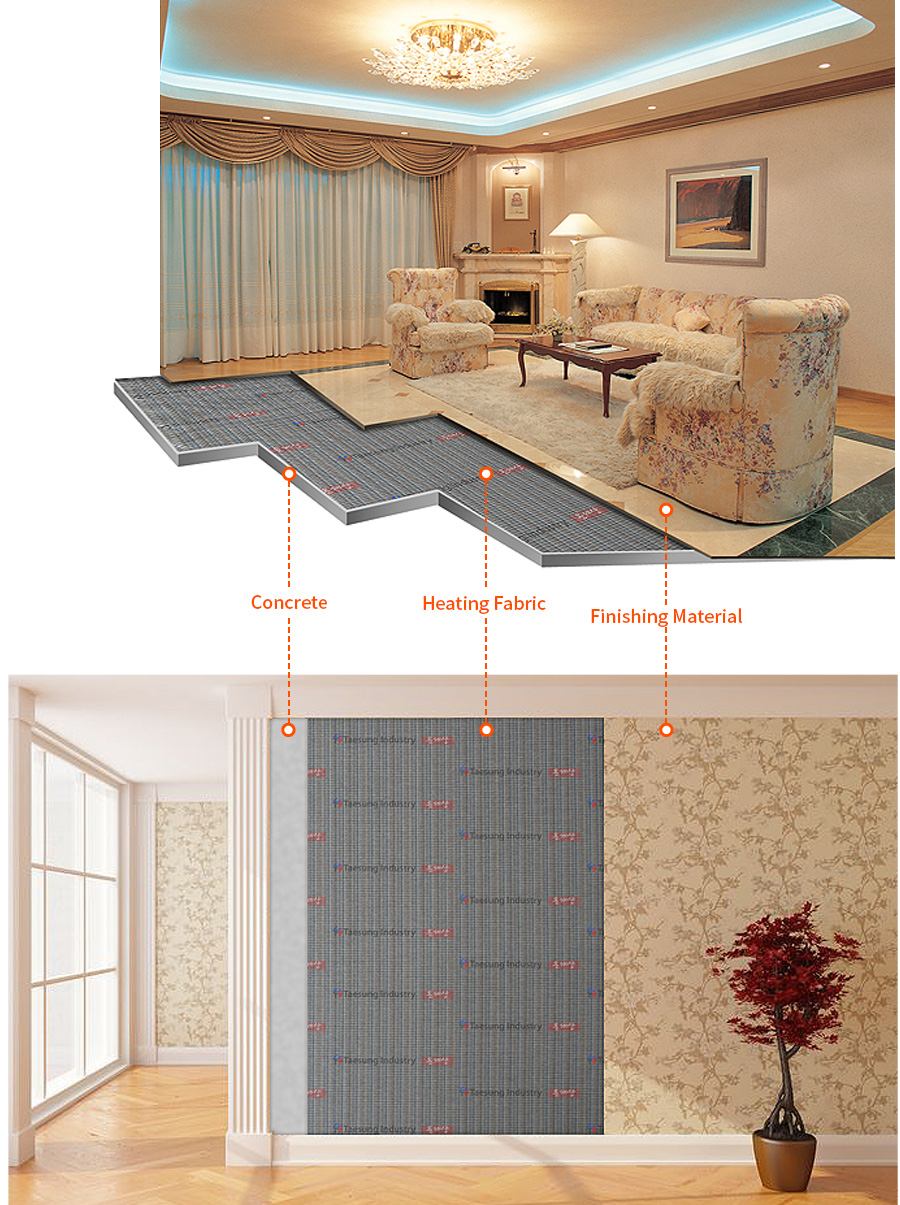
Application of product for heating
There are various fields that can be applied to the Heating Fabric (high-tech new material for heating produced by Korean company) that emits far-infrared rays, and the scope of application is as follows.
- Heating for new and existing buildings (hotels, restaurants, coffee shops, banks, apartments, pensions, offices, private houses, etc.): Applicable to any ceiling or floor, dry and wet heating available.
- Sauna
- Paintings heater
- Mat
- Clothing
- Cushions, cushions for wheelchairs and strollers, cushions for pets, etc.
- Botanical gardens, farms, etc.
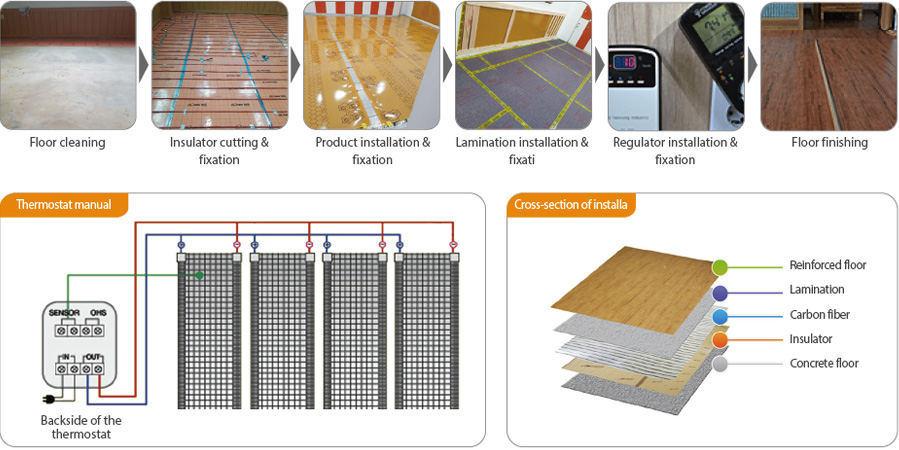
How to Install
A semi-permanent economic heating system that is easy to install
We accurately measure the place to install heating and draw up an installation range of the heating product and an installation floor plan. After calculating the power consumption, we thoroughly check the installation place and contract demand before beginning the installation.
Installation Procedure
Places to install fiber heating: churches, diners, apartment extensions, studio apartments, school dormitories, containers, small accommodation rooms for students studying for exams, schools, hostels, hotels, accommodations, fitness clubs, daycare centers, senior citizens’ community centers, nursing homes, hospitals, county houses, restaurants, etc.
Feature Comparison Chart of Each Heating Element Type
| Item | Electric panel | Metallic general heating element |
Carbon-film surface heating element |
Heating Fabric (TAESUNG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing method | Electric-pad-style coil type | Utilizes a copper heating rod | Prints a carbon heating element on the PET film and then processes with lamination | Produces excellent heating textile with the carbon heating yarn of a highly precise resistance value |
| Method of heat release | Conductive heat transfer (3 min of heating Temperature difference in the heated surface | Conductive heat transfer (3 min of heating) Temperature difference in the heated surface | Radiant heat transfer | Radiant heat transfer method (heated concurrently with power connection) |
| Thermal efficiency | Maximum heat of 50-60°C Thermostat must be attached | Maximum heat of 90-120°C Thermostat must be attached | Maximum heat of 80°C Thermostat must be attached | Maximum heat of -150°C Thermostat can be selectively attached |
| Thermal properties | Ignites in high temperature, burns the human body | Connections become blazed in a high temperature ▶ risk of ignition, unable to maintain combustion | No burning even in a high temperature ▶ secures safety | |
| Safety | Electric shock/leakage from fire and moisture caused by using low-quality heating cables | Risk of fire due to the adhesion of electrode wires | Risk of fire and lack of lifespan assurance due to the separation of electrode wires during prolonged use |
When the woven fiber material is damaged, only the damaged part is disconnected, ensuring semi-permanency and safety |
| Economics | Overconsumption of power ▶ Excess cost is incurred Restrictions of power lines ▶ Limited installation | Overconsumption of power ▶ Excess cost is incurred Restrictions of rod sizes ▶ Limited installation | Overconsumption of power ▶ Excess cost is incurred Restrictions of film sizes ▶ Limited installation | An even heat distribution reduces power consumption and maximizes heat conduction and heat efficiency Free size control of the installation area |
| Space heating | Unavailable | Insignificant | Insignificant | Highly superior |
| Risk | Exposure to electromagnetic waves | Exposure to electromagnetic waves | Little electromagnetic waves. Insignificant release of far-infrared rays | Fundamentally generates no electromagnetic waves. Releases the largest amount of farinfrared radiation heat |
| Permanency | Creases cause short circuit Unrecyclable, inconvenient storage | Difficult to preserve and maintain, unrecyclable | Easily damaged, loses function when damaged, unrecyclable | Freely altered and processed as a fiber material and easy to store, recyclable |
| Heating structure | Conducted heating | Conducted heating | Straight anaerobic heating (flat heating) | Radial anaerobic heating (hexangular heating) |
| Penetration of far-infrared rays | Generates harmful electromagnetic waves | None | Insignificant | Practical radiation of massive far-infrared rays |
| Effect of far-infrared rays | None | None | Partial rupture | Eradication and deodorization of harmful bacteria like mites and mold |


